
Causes of kaolin formation in white mud bed

Kaolinite deposition from moving suspensions: The
2022年8月23日 This study represents a systematic flume study of the factors that control the formation of bedload floccules and bed accretion in moving kaolinite suspensions A key result is that up to suspended sediment 2017年1月1日 This paper sheds more light on genesis and evolution of the kaolin minerals in white sandstones of the Lower Paleozoic Naqus Formation (PDF) The Nature, Origin and Distribution of Kaolinite 2022年8月23日 The need for a better grasp of underlying processes is acute, given recent flume studies that show that moving suspensions form large bedload floccules, migrating floccule (PDF) Kaolinite deposition from moving suspensions: The roles of 2019年10月1日 At 5 cm below the surface of the soil, kaolin migrates rapidly to the surface along the channels and forms a series of white accumulation The phenomena of group C and D are Pumping effect of waveinduced pore pressure on the

Accretion of Mudstone Beds from Migrating Floccule Ripples
Formation of floccule ripples from a variety of claysize materials (kaolinite, montmorillonite, and lake mud), and over a range of sediment concentrations and salinities (distilled, fresh, and salt 2011年6月17日 This paper investigates the behaviour of rapidly decelerated to steady flows that contain a mixture of sand, silt and clay, and explores the effect of different clay (kaolin) Depositional processes, bedform development and hybrid bed 1991年12月1日 The Upper Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Whitemud Formation is a potentially commercial kaolin deposit located in southern Saskatchewan and southeastern Alberta The Clay Mineralogy, Alteration History, and Economic Geology of the 2006年8月1日 During the settling process there are several factors that affect the settling behaviour of the kaolinite suspension: (i) particle size, (ii) solid/water concentration, (iii) Settling and sediment bed behaviour of kaolinite in aqueous media

Kaolin: Soil, rock and ore : From the mineral to the magmatic
2016年10月1日 The organic matter has no effect on the formation of kaolin in the primary deposits In the secondary kaolin deposits the mediating effect increases from the residual This deep chemical weathering altered the volcanic tufts into kaolinitic clay at the source area; the kaolin of the Whitemud Formation is not derived from the weathering of feldspars at the site of MINERALOGY AND ORIGIN OF THE EASTEND AND WHITEMUDRenewable biomass fuels are frequently used for power generation Biomass ash causes bed agglomeration in fluidized bed boilers due to the formation of alkali silicate melts Very few prior studies have tested dolomite and kaolin bed additives for agglomeration mitigation with agricultural biomasses In this work, pelletized miscanthus and wheat straw were tested in a The use of kaolin and dolomite bed additives as an of large amounts of wastes, in this case, very finegrained kaolinite (white mud) The research aimed to find a final destination for such residues by developing new building materials The proposed material is a pozzolanic pigment produced through calcination and grinding of mixtures of red mud and kaolin wasteThe Use of Red Mud and Kaolin Waste in the Production of a
Geopolymers in construction Recent developments
formation of a gel like structure and due to condensation, large networks are formed by oligomers in the aqueous stage This process results in the release of water which helps in the formation of a hydrated gel This gel structure is termed as biphasic, with the aluminosilicate binder and water as the two phases2013年1月15日 The erosion threshold of sandmud mixtures is investigated by analyzing the momentum balance of a sand particle or a mud parcel in the mixture bed surface, and a formula for the critical shear Bedform development in mixed sand–mud: The contrasting role 2000年3月23日 Agglomeration of bed material and fuel ash may cause problems during fluidized bed combustion of biomass fuels Previous results have shown that a “sticky” coating, which covered the original bed material and consisted of CaKsilicates, was directly responsible for the bed agglomeration during biomass combustion The melting behavior (stickiness) of these The Role of Kaolin in Prevention of Bed Semantic Scholar2010年4月19日 Physical remediation involved turning the filter media and scraping mud balls from the filter bed Chemical remediation involved the in situ application of chlorine, and hydrogen peroxide onto the Practical means of solving mud ball problems in sand filter media
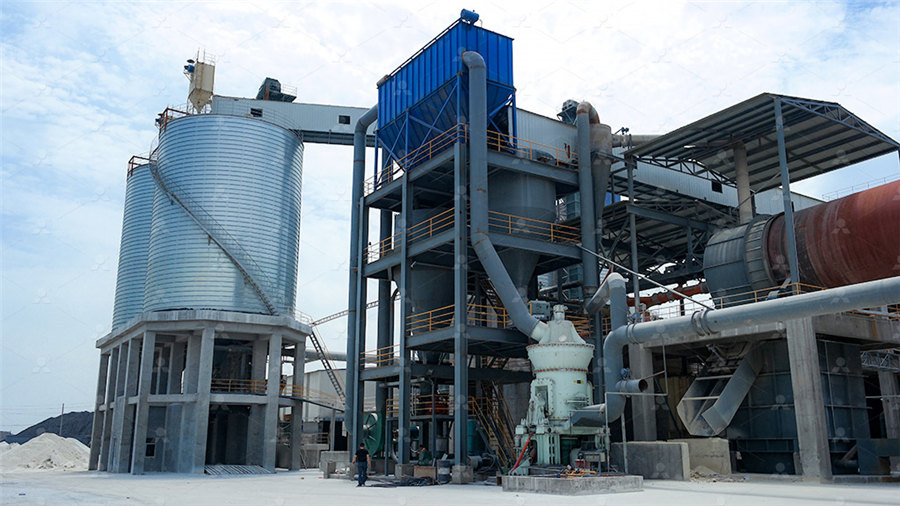

An overview of kaolin and its potential application in
2023年8月1日 Kaolin is a sedimentary rock that is rich in the mineral kaolinite This claylike mineral is what gives kaolin its white colour Kaolin deposits can be found in locations all over the world These deposits are classified into two categories, that 2022年7月1日 Biomass ash causes bed agglomeration in fluidized bed boilers due to the formation of alkali silicate melts Very few prior studies have tested dolomite and kaolin bed additives for agglomeration The use of kaolin and dolomite bed additives as an 2017年1月1日 This paper sheds more light on genesis and evolution of the kaolin minerals in white sandstones of the Lower Paleozoic Naqus Formation at Wadi ElDakhel and Wadi Qena along the western side of the (PDF) The Nature, Origin and Distribution of Kaolinite in the Lower The clay fractions of sedimentary kaolin deposits representing different ages (Carboniferous and Cretaceous), types (pisolitic flint and plastic), and localities (Sinai and Aswan) from Egypt were (A) Lithostratigraphy of the kaolin depoaits in the Aswan area
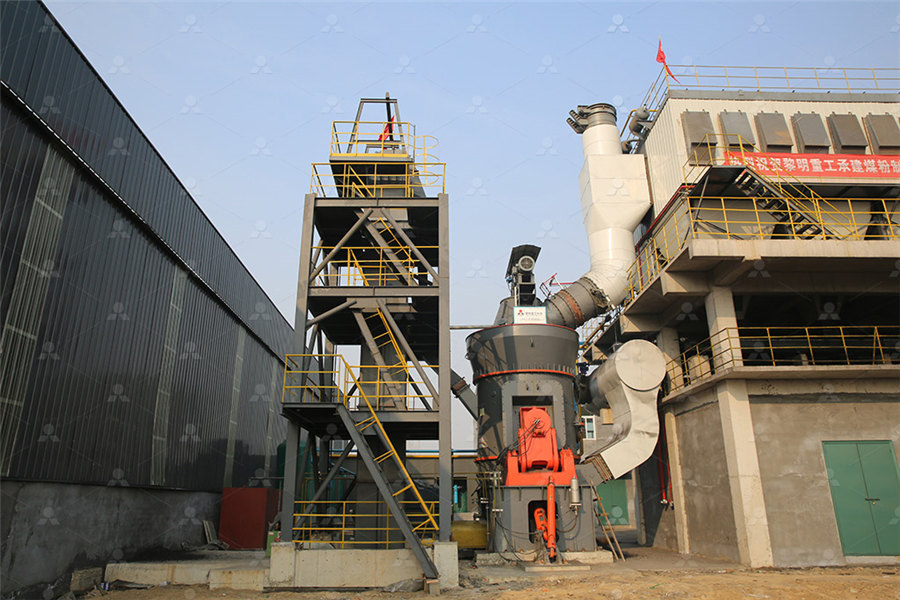

Depositional processes, bedform development and hybrid bed formation
2011年6月17日 This paper investigates the behaviour of rapidly decelerated to steady flows that contain a mixture of sand, silt and clay, and explores the effect of different clay (kaolin) concentrations on the dynamics of flow over a mobile bed, and the 2013年4月1日 Kaolin is mostly associated with minor quantities of ferruginous and carbonaceous impurities which impart color to this white mineral Hence, their removal is of prime importance in the value Influence of iron on the occurrence of primary mullite in kaolin is responsible for the generation of red mud, a wellknown residue from Bayer process The kaolin processing plants are also responsible for the generation of large amounts of wastes, in this case, very finegrained kaolinite (white mud) The research aimed to find a final destination for such residues by developing new building materialsThe use of red mud and kaolin waste in the production of a new 2018年1月15日 Request PDF Depositional processes, bedform development and hybrid bed formation in rapidly decelerated cohesive (mud–sand) sediment flows Flows with high suspended sediment concentrations Depositional processes, bedform development and hybrid bed formation
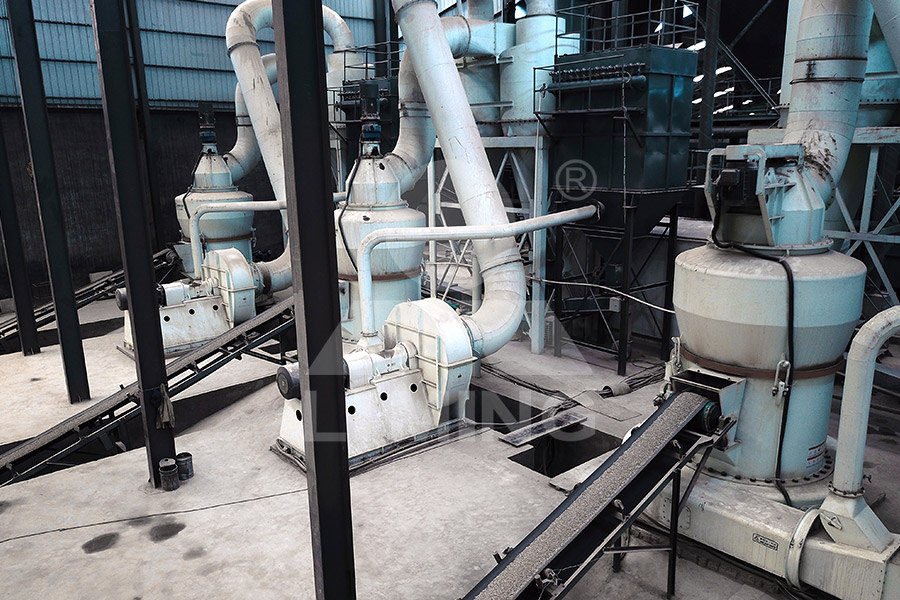

Clay Mineralogy, Alteration History, and Economic Geology of the
1991年12月1日 The Upper Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Whitemud Formation is a potentially commercial kaolin deposit located in southern Saskatchewan and southeastern Alberta The Whitemud Formation contains a lower kaolinitic sandstone, a middle lignite and carbonaceous shale, and an upper interbedded siltstone and claystone The sediments that comprise the Bedding and lamination The most common feature of sedimentary rocks is that they are organized in layers of different composition piled on top of each other Any layer of rock in a sedimentary sequence that can be distinguished from the layers above Bedding and lamination – Geology is the Way2020年7月6日 Mud has long been thought to constitute the washload—the portion of river sediment loads that settles too slowly to actively interchange with or be sourced from the sediment bed 1,2Unlike the Mud in rivers transported as flocculated and suspended bed 2019年6月7日 Example of steady state flow curves measured for 40% aqueous kaolin suspensions without (black) and with SHMP additive (02% grey, 05% white symbols)(PDF) Deflocculation of Kaolin Suspensions ResearchGate
.jpg)
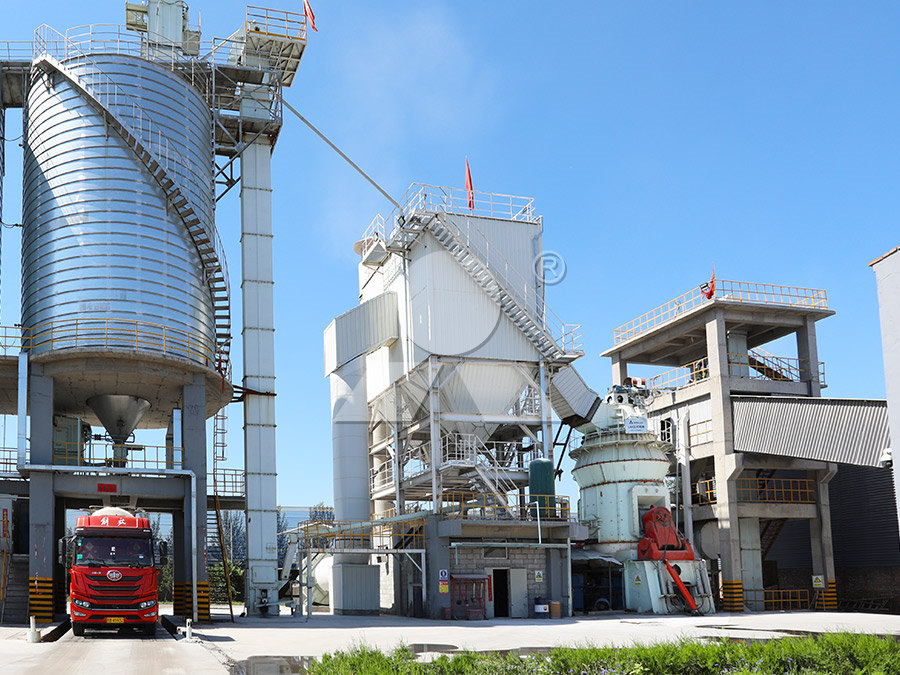
Mineral Planning Factsheet Kaolin
Kaolin Mineral Planning Factsheet China clay or kaolin is a commercial clay composed principally of the hydrated aluminosilicate clay mineral kaolinite The term kaolin is used here The commercial value of kaolin is based on the mineral’s whiteness and its fine, but controllable, particle size which may be optimised during processing Particle2021年7月16日 of white cement and fireproof materials, in drilling (mud), hydroinsulation of landfill sites, hydroinsulation of rock mass, and recultivation of sandy soil, as well as adsorbents of organic Calcination of Clay Raw Materials in a Fluidized Bed2024年3月28日 This study evaluates the formation of hydrothermalorigin kaolingroup minerals by considering their characteristics of hydrothermal alteration, isotopic compositions and differences in (PDF) Global Occurrence, Geology and Characteristics 2023年10月16日 The aims of this paper are to: (i) investigate the effect of mud bed rheology on the formation and preservation state of continuous tool marks; (ii) determine the formation mechanism of striated groove marks; (iii) delimit the rheological properties of the bed, necessary for the generation and preservation of continuous tool marks; and (iv) determine how the Sedimentology Wiley Online Library

The use of kaolin and dolomite bed additives as an
2022年8月1日 Biomass ash causes bed agglomeration in fluidized bed boilers due to the formation of alkali silicate melts SEM image of a crosssection of a pellet shaped agglomerate collected following a test with wheat straw and 150% kaolin The overlaid cylinder in white is the hypothetical position of the core of the wheat straw pellet 2006年8月1日 Kaolinite and quartz are the common gangue minerals found in raw coal; however, their effects on stability of coal froths and subsequent settling of coal flotation products have not been investigatedSettling and sediment bed behaviour of kaolinite in aqueous Abstract High alkali and alkali earth metals (AAEMs) content in coal causes severe slagging and fouling during combustion in a boiler In this study, the ash deposition behavior of a highalkali coal at different bed temperatures and the effect of kaolin were investigated in a 30 kW circulating fluidized bed (CFB) test system using an ash slagging probe and deposition probeAsh deposition behavior of a highalkali coal in circulating 2011年6月17日 This paper investigates the behaviour of rapidly decelerated to steady flows that contain a mixture of sand, silt and clay, and explores the effect of different clay (kaolin) concentrations on the dynamics of flow over a mobile bed, and the Depositional processes, bedform development and hybrid bed formation
.jpg)
Ash characteristics of oxybiomass combustion in a circulating
2021年9月1日 A good bed material for use in a CFB will not only obtain a low attrition index (AI) but also a low strength index (SI) and will be unaffected on the surface of the cyclone and watersteam tube Therefore, the AI and SI of the sampled ashes from oxyCFBC, operating with kaolin addition, are useful to evaluate kaolin as a bed material additiveRoughly 5000 years ago, the Laohuling Dam was constructed in Liangzhu using a grasswrappedmud technique commonly used in waterfront construction at this time We conducted our observation and sample collection at the Laohuling Dam site in order to better understand the mechanisms underlying the formation and transformation of grasswrappedmud tracesMechanisms of formation and change in grasswrappedmud 2021年9月10日 1 Introduction Largediameter slurry shields are widely used in urban tunnel engineering and sea (or river) crossing traffic tunnel engineering [1 – 3]During shield construction, the mud slurry penetrates soil and forms a mud filtration cake on the excavation surface, which can balance the pressure of water and soil in the ground; thus, the excavation Experimental Study on the Formation and Characteristics of Mud The strongest experimental evidence for the influence of cohesive clay on the development of bedforms and their primary current stratification below rapidly decelerated mud–sand flow includes the following: (1) heterolithic stratification comprising alternating laminae or layers of sand and mud (eg Fig 20); (2) the preservation of lowamplitude bedwaves (eg Fig 19), Predicting bedforms and primary current stratification in cohesive
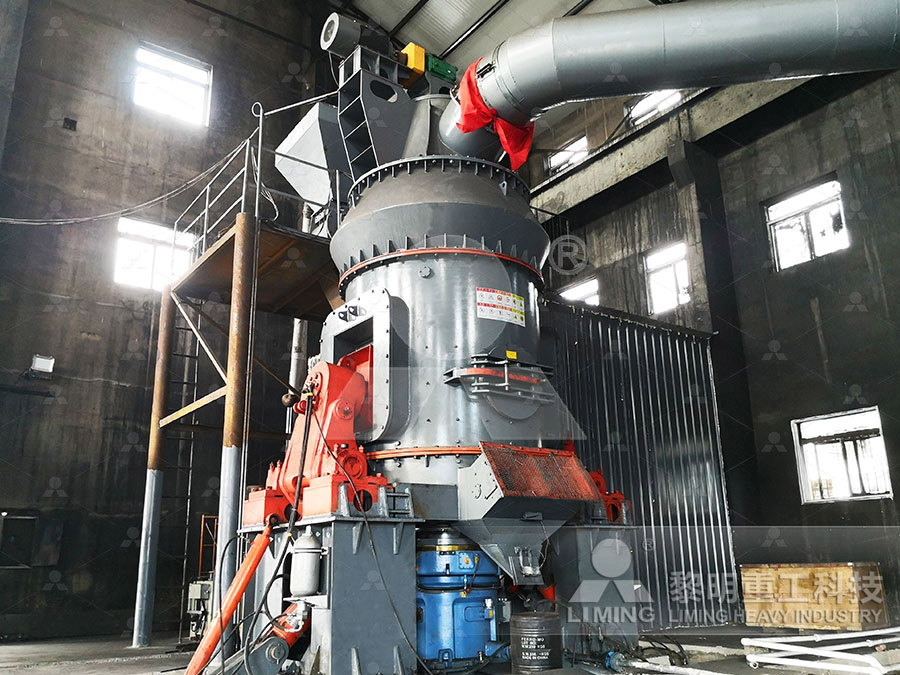

Mineralogy, Geochemistry, and Genesis of Kaolinitic Springer
2021年4月14日 Grayblack kaolinitic claystones of industrial value are abundant in Upper Carboniferous–Lower Permian coalbearing strata of the Datong Coalfield of northern China The main types are tonsteins and cryptocrystalline kaolinitic claystones, distinguished by the thinness and greater crystallinity of kaolinite in the former and by the presence of detrital illite and 2012年9月23日 required to cause considerable redistributions of aggregated kaolin flocs within sediment beds with 04dwb% PEI For example, with 6 and 18 shear revolutions within sediment beds with(PDF) SEDIMENTATION OF KAOLIN: EFFECTS OF deposition of the host bed, the emphasis in this paper is on the first of these causes – sedimentation – whilst not precluding postdepositional causes in other environments (eg Owen et al, 2011) Early authors (eg Kuenen Migliorini, 1950; Ten Haaf, 1956) alsoThe formation of convolute lamination in mudrich turbidites2011年3月30日 [1] Mud peeling is a common phenomenon whereby horizontal cracks propagate parallel to the surface of a drying clay Differential stresses then cause the layer of clay above the crack to curl up to form a mud peel By treating the clay as a poroelastic solid, we analyze the peeling phenomenon and show that it is caused by the gradient in tensile stress at the surface Mud peeling and horizontal crack formation in drying clays
.jpg)
(PDF) Formation Mechanism of Mud Volcanoes/Mud Diapirs Based
2021年7月26日 The formation of mud volcanoes/mud diapirs is directly related to oil and gas accumulation and gashydrate mineralization Their eruptive activities easily cause engineering accidents and may 2004年6月1日 Examined in terms of the ternary diagram silicaaluminaother oxides of Fabri and Fiori (1985), most of the kaolin samples plot into the white stoneware field (Fig 6, from Papoulis et al 2004)Progressive Stages in the Formation of Kaolin Minerals of 2019年10月1日 At 5 cm below the surface of the soil, kaolin migrates rapidly to the surface along the channels and forms a series of white accumulation The phenomena of group C and D are most obvious (Fig 4 b) At first, the white kaolin upwells in group D, and then the color gradually deepens to the normal silt upwelling, gradually covering the white kaolinPumping effect of waveinduced pore pressure on the development of 2024年1月29日 Subgrade mud pumping is a worldwide problem that seriously threatens railway track stability and operational safety This paper analyzes the influence of Kaolin content (plasticity index) on the characteristics of saturated subgrade mud pumping under cyclic loading using a selfdeveloped test model Test samples consist of clay mixed with 10%, 20%, and Study on characteristics and mechanism of subgrade mud
.jpg)
Critical Shear Stress for Erosion of SandMud Mixtures and Pure Mud
where τ cr is the critical shear stress of sandmud mixtures; p m is mud content; p mcr is the critical mud content (about 10–15%), below which the mixture is cohesionless and above which the mixture exhibits cohesion; τ crs and τ crm are the critical shear stresses of pure sand and pure mud, respectively; β v is an empirical coefficient between 075 and 1252013年1月15日 Temp = mean water temperature f 0 = initial dry weight mud fraction in bed sediment f e = final dry weight mud fraction in bed sediment h = flow depth above the sediment bed U ¯ ¯ = depthaveraged flow velocity u * = shear velocity z 0 = bed roughness length τ b = bed shear stress Fr = Froude number Re = flow Reynolds number after Liu and Mei (1990)Bedform development in mixed sand–mud: The contrasting role of













